Replacing your GPU cooler isn't rocket science, but we're dealing with expensive hardware so follow these steps carefully. Don't skip, rush or overtighten anything and you should be good.
If you need support at any point, feel free to join the discord or contact me on the bottom of the support page.
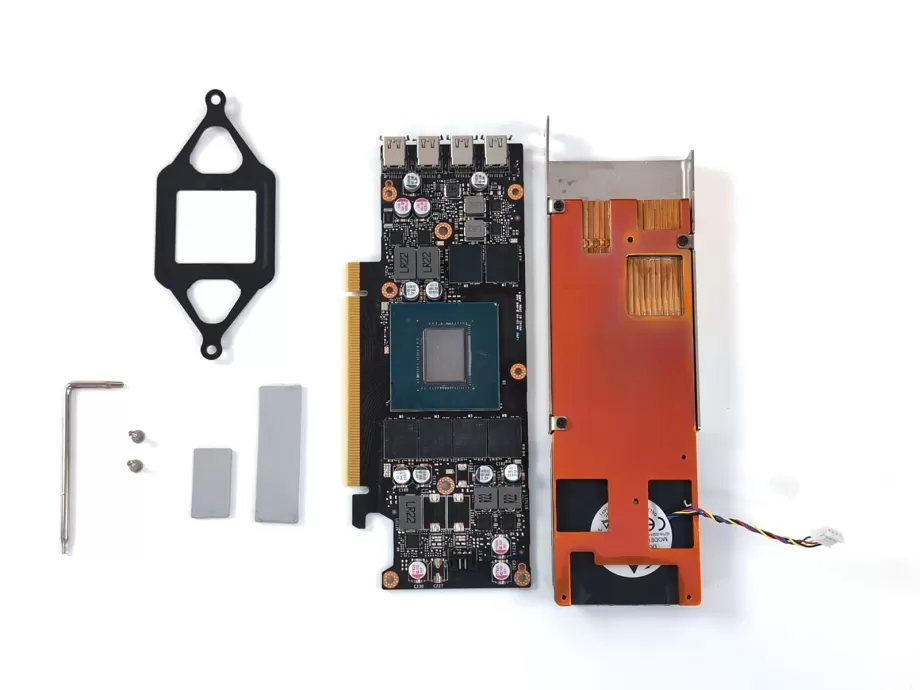
Preparations
You should've received your cooler along with some accessories. Make sure the box contains the following:
- Cooler
- PCIe bracket
- Thermal pads
- M2.5 shoulder screws
- M2 screws (2 for A2000, 8 for Ada cards)
- T6 and T8 screwdriver
You will need to provide for yourself:
- Phillips screwdriver (PH1 preferred)
- Thermal paste
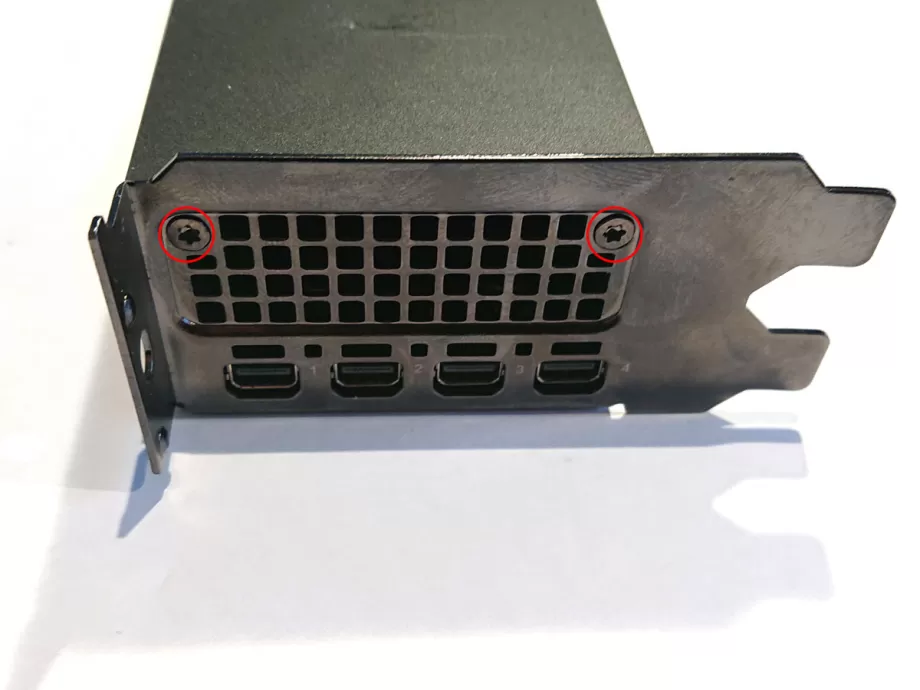

1.Remove the PCIe bracket screws
The first screws to remove are the two screws that hold the PCI bracket to the shroud. They are both T8 screws, which is the largest screwdriver of the two included.
Don't pull off the PCIe bracket just yet, as it's still fixed to the PCB.
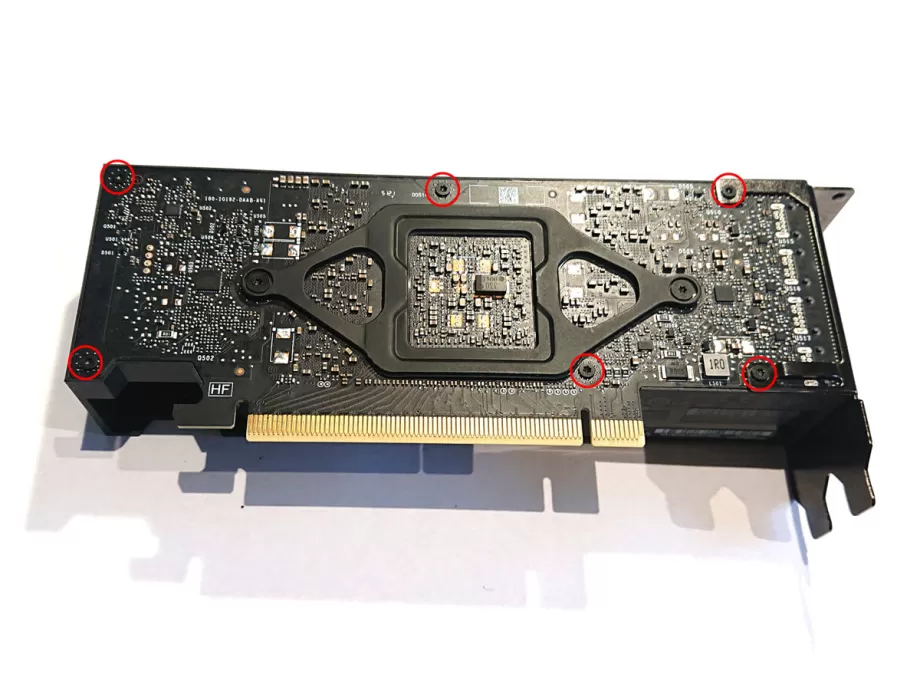
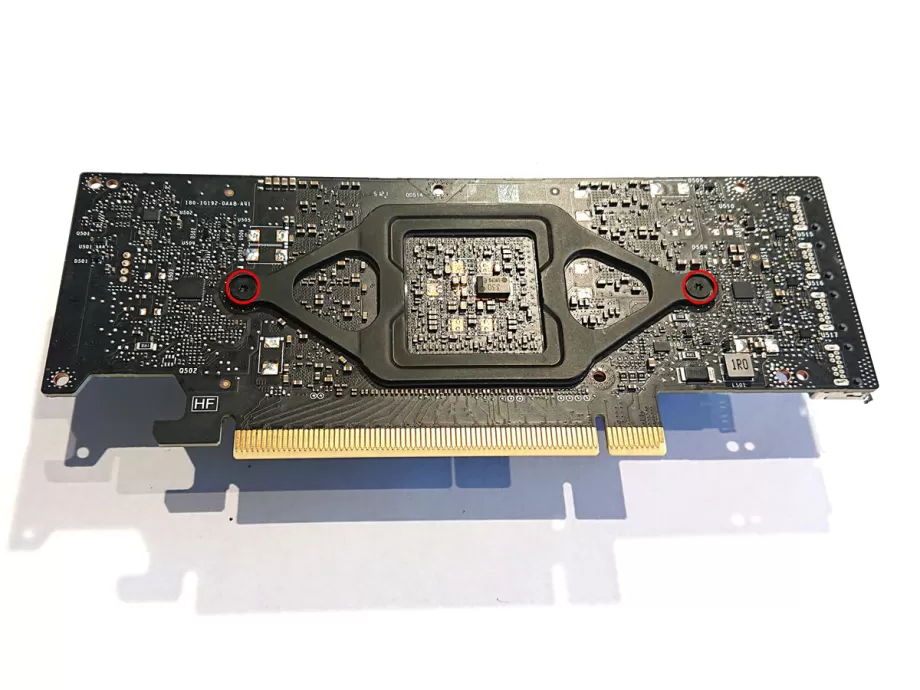
2.Remove the shroud
To remove the shroud, we need to unscrew all screws, apart from the larger ones in the retention bracket. They are all T6 screws.
Unscrew the right two screws first, as they are the ones still keeping the PCI bracket in place. You can take off the bracket and then unscrew the rest of the screws.
RTX 2000 Ada and 4000 Ada owners will be able to take off the backplate at this point.
Lift the shroud a little bit and carefully detach the fan header. This may require small pliers. When the header is detached, you can take off the shroud.

3.Remove the stock heatsink
The heatsink is attached with T6 screws through the retention bracket. When unscrewing those, be wary that there is quite some force on the bracket, and it springs back when it comes loose. You want to hold it back when unscrewing the screws in order not to damage things. When all screws are gone, you can take off the heatsink. It may be glued to the die due to the thermal paste, carefully tilt it to the left and right until it comes off in that case.
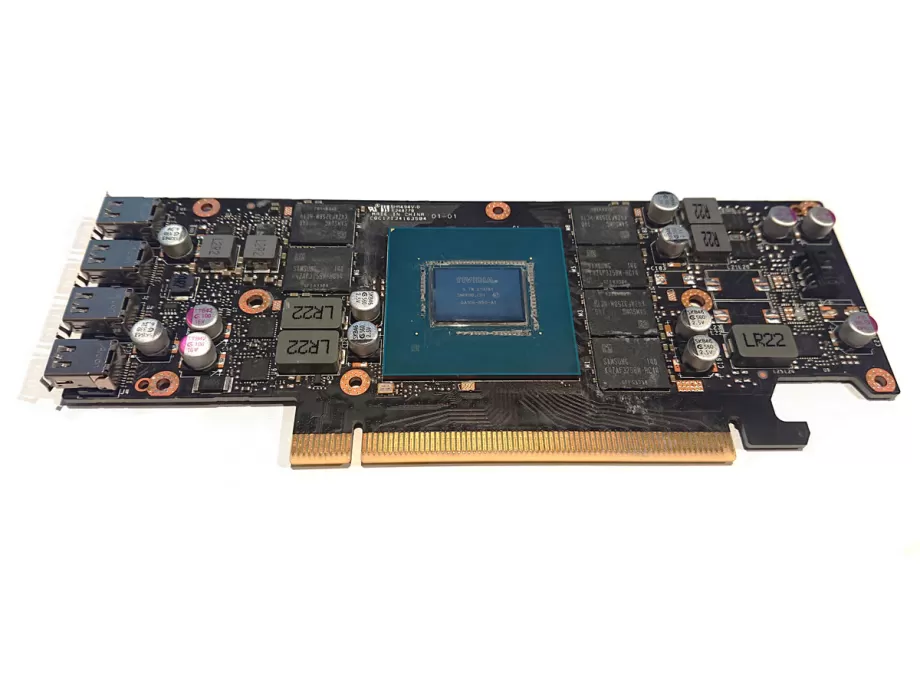
4.Clean the die and memory
Wipe the original thermal paste off the die using a lint free cloth. Clean the die using a bit of Isopropyl or other cleaning alcohol.
For the A2000, the original thermal pads are bad and should be replaced. They are brittle and probably come off in multiple pieces. You can use some Isopropyl here too.
The Ada generation cards have better pads. We will only replace the ones from the top of the pcb, the backplate ones can stay in place.
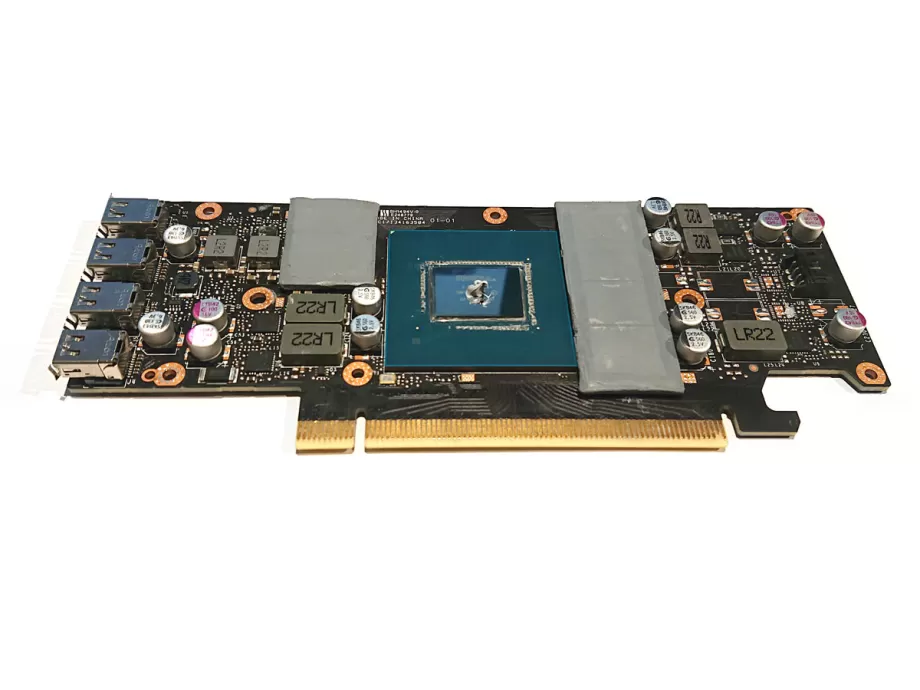
5.Thermal pads and paste
Put a small drop of thermal paste on the die, about the size of a grain of rice. Next, put the thermal pads on the memory chips. The pads are already cut to size, but don't forget to take the plastic off both sides.
For Ada generation cards, you only need to replace the thermal pads between the card and the cooler. For the back, you can reuse the original ones.
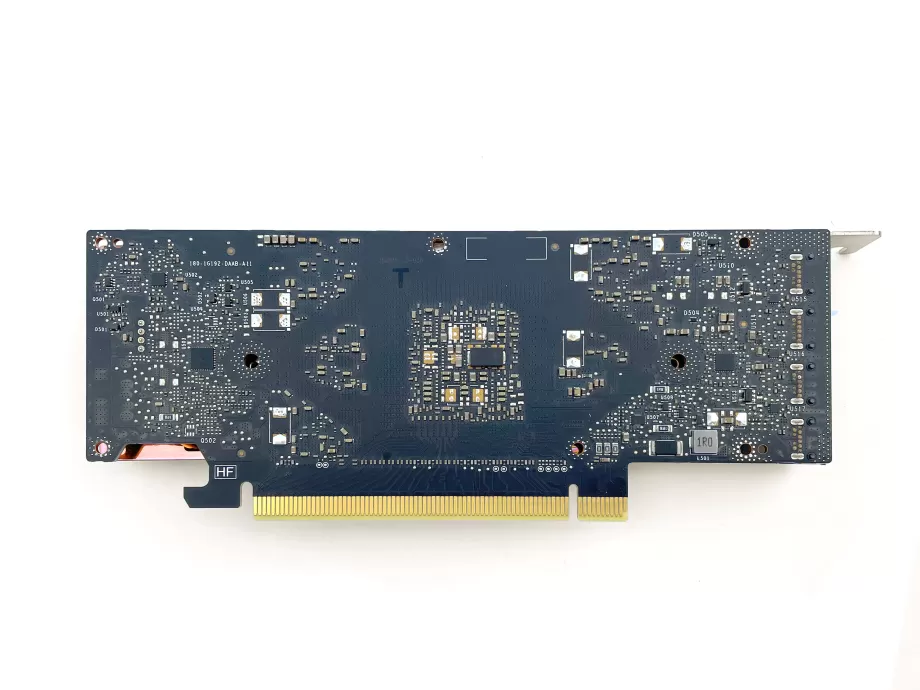
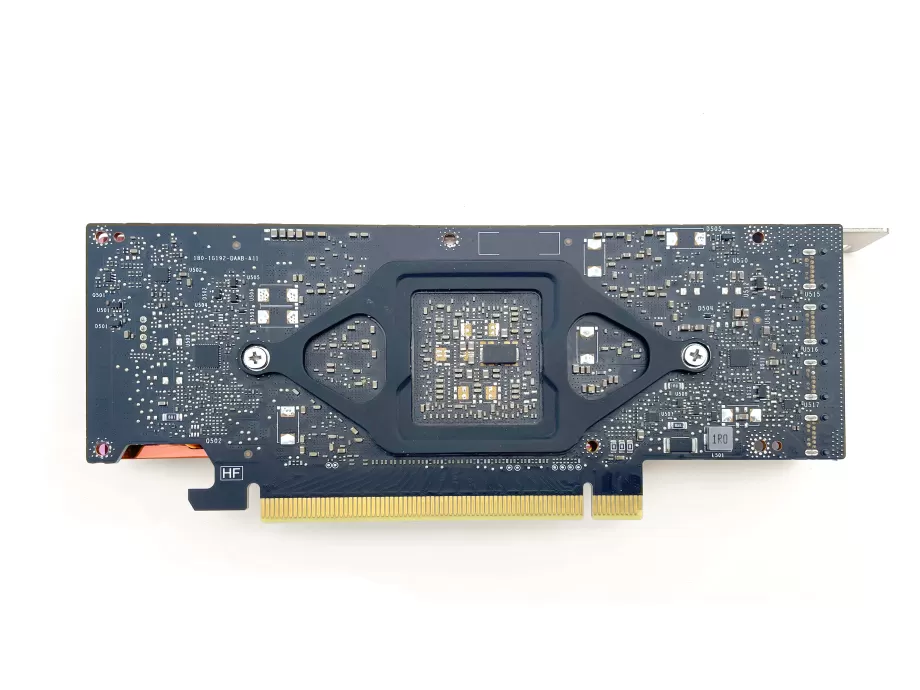
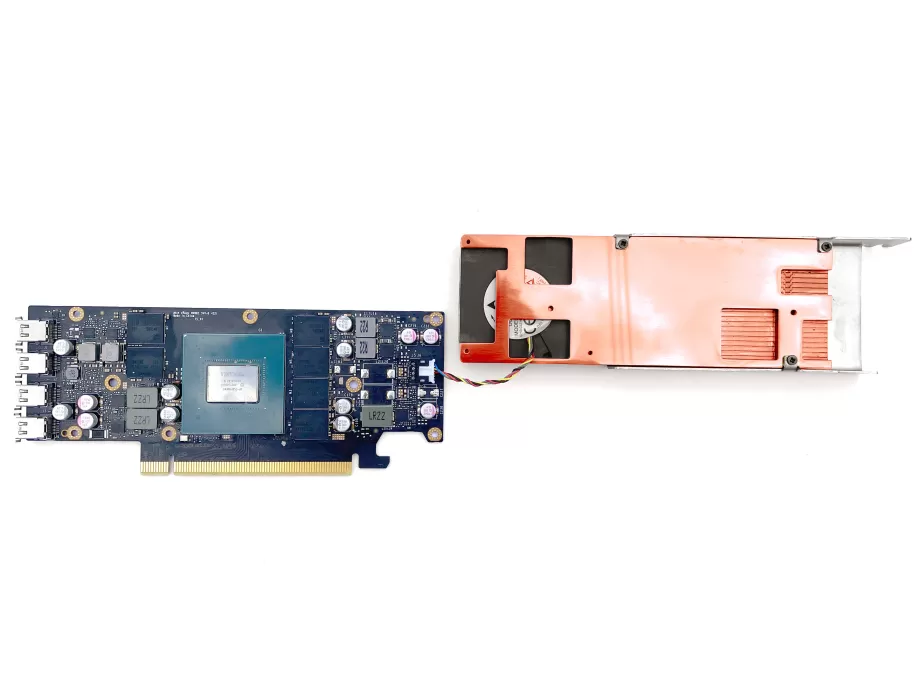

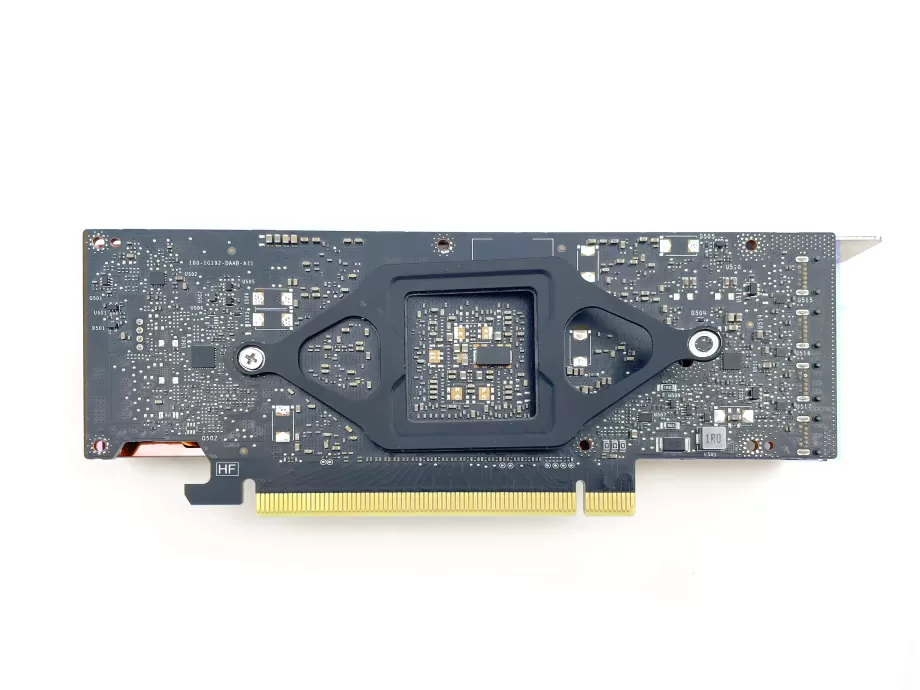

6.Mount the cooler
Lay the cooler upside down, with its fan against the back of the card and plug in the fan header. Pivot the cooler into place on the card. Turn around the card along with the cooler so you can mount the cooler to the card.
Put the retention bracket into place and screw the shoulder screws through the bracket and PCB into the cooler. You will have to squeeze the bracket and the cooler together to do so. It requires some force, be careful not to put force on the PCB or the fan as they are fragile.
When all screws are in place, gently tighten them until you can't screw them in any further. There are 'shoulders' on the screws which prevent you from screwing them in too far.
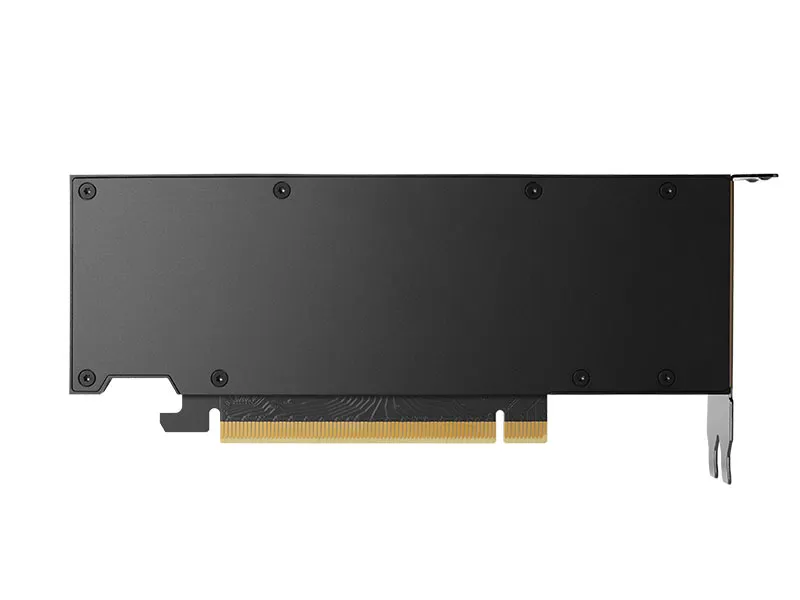

8.Backplate
Ada generation cards now need to attach the backplate. Use the eight included M2 screws and not the original ones, as they are too long.
Don't forget to put the PCIe bracket between the pcb and backplate before you screw in the 2 screws on the front of the card.
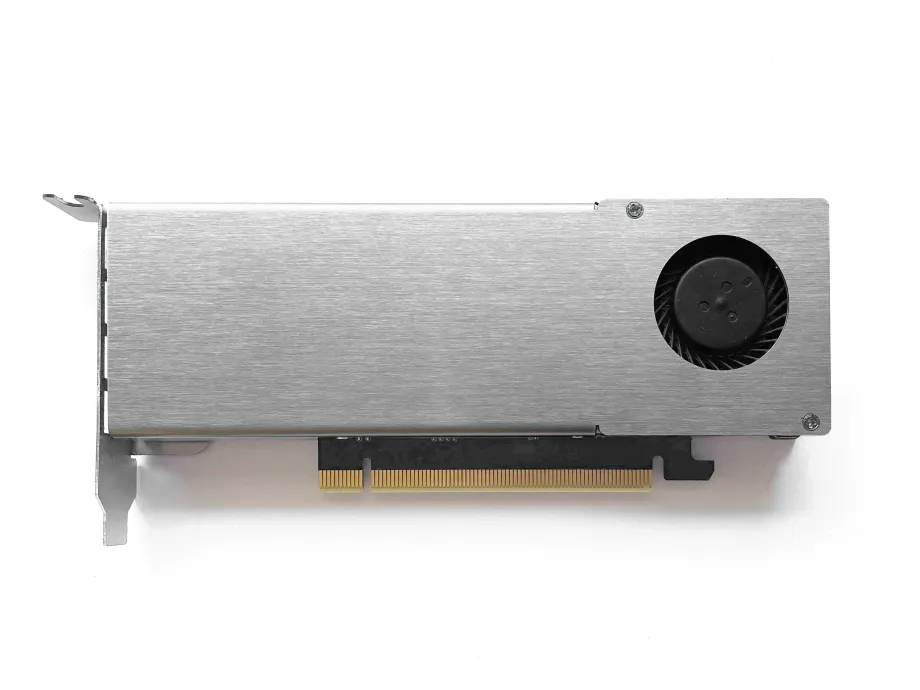

10.Cooler installed!
You have successfully installed the single slot cooler! You can now start using the card, but there are some next optional software steps to tweak it a bit.
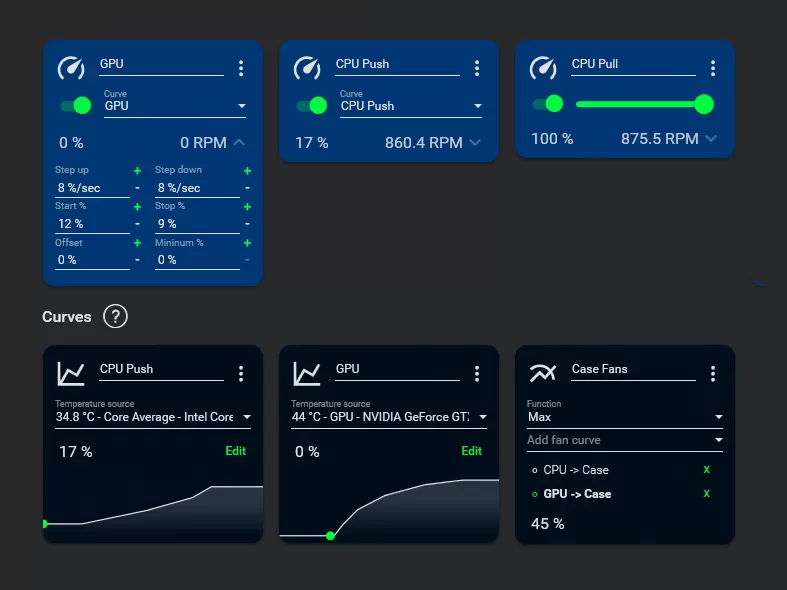
11.(Recommended) fan curve
The stock fan keeps the fan runnig at low speeds, even when the card is running hot. While a fan curve may be up to personal preference, I advice a linear or exponential curve that increases the fan speed from 30% to 100% between 40°C and 80°C.
Custom fan curves can be configured using software like Fan Control or MSI Afterburner and require a recent driver version (Game Ready or Studio).
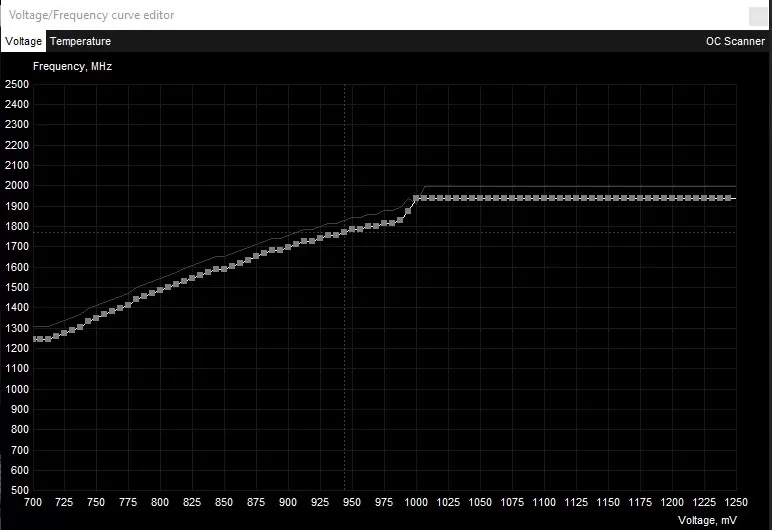
12.(Recommended) Undervolt
Undervolting your card means tweaking the voltage the chip uses at a chosen frequency. Chips usually have a very conservative voltage/clock speed ratio, meaning you can reduce the voltage a lot without reducing the clock speed by a lot. Your card will draw less power, run cooler and more silent and be more power efficient.
While not required, cooling the card with such a small cooler is challenging so it will benefit from the reduced power draw. For an in-depth guide on undervolting, please refer to this article.
Do you want a single slot card too?
Purchase the single slot cooler and follow this guide to enjoy the tiniest possible RTX A2000 or RTX 4000 SFF!